"CSP-FoSyS" activity, second phase started!

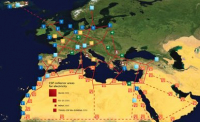
Did you know that the energy coming from the sun everyday and reaching the surface of the Earth is equivalent to 60,000 times the worldwide energy consumption per day? The potential of the sun to cover the worldâs electricity needs is immense, but it is not equally distributed, depending on the area of the globe and the meteorological conditions, whereas the areas with better solar resources are not always the largest electricity consumers.
 As an example, Dr. Gerhard Knies, chairman of the Supervisory Board of the DESERTEC foundation, explains us:
As an example, Dr. Gerhard Knies, chairman of the Supervisory Board of the DESERTEC foundation, explains us:
- âWithin 6 hours, deserts receive more energy from the Sun than humankind consumes within a year. But how can this radiant energy be economically transformed into useful energy and transported to consumers?â
Even with this limitation, huge investments are made in solar transducer technology like photovoltaic panels, parabolic-through reflectors, solar towers etc.
In the short term, considering the current status of the technology, Concentrating Solar Power technology (CSP) based on parabolic through reflectors is seen as one of the clearest options for the future, as it allows the generation of electricity on large scales. Sunny regions of Europe are experiencing the deployment of the first of these power plants, supplying energy to their surrounding areas. Solar Millennium AG together with partners has developed, designed and realized Europeâs first CSP power plants, located in the region of AndalucÃa, near Granada, Spain, and they describe us their working principle:
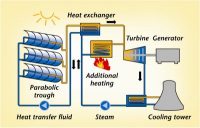
 - âThe technology is based on the concentration of direct solar radiation using parabolic-shaped mirrors.â says Benedikt Pulvermüller, project manager at Solar Millennium AG. The heat is collected in an absorber tube filled with a heat-transfer fluid.The heat is used to generate steam which is used to run a turbine and to produce electricity as in many other conventional power plants, like coal or gas. The rationale behind this approach is that heat can be easily stored and later used to generate additional steam, particularly during cloudy periods or even at nightâ
- âThe technology is based on the concentration of direct solar radiation using parabolic-shaped mirrors.â says Benedikt Pulvermüller, project manager at Solar Millennium AG. The heat is collected in an absorber tube filled with a heat-transfer fluid.The heat is used to generate steam which is used to run a turbine and to produce electricity as in many other conventional power plants, like coal or gas. The rationale behind this approach is that heat can be easily stored and later used to generate additional steam, particularly during cloudy periods or even at nightâ
Andasol-1 was designed with a production capacity of 50 MW, allowing a maximum production up to 180 GWh per year. However, radiation received by the power plant is rather variable due to night, clouds or aerosols. In order to optimise the operation of the power plant and take the most out of it, a proper forecasting system is required. There it is where space technologies enter on stage. Data coming from Earth Observation satellites can be used to support standard weather forecasts and local measurement stations, while satellite telecommunications can make all the information from the satellites and the ground stations available in real time, which is a mandatory requirement for the operation of the power plant.
However, if the storage of heat allows the provision of a stable electricity output, why is it necessary to develop a forecasting system? Just because it is not enough to grant stability on a theoretical basis. Electricity grid and market operators have tight requirements of predictability over long periods of time. If renewable energies have to enter into real operation on massive scales, stability is an imperative to avoid a general collapse of the electricity distribution system. Additionally, it will allow the planning of maintenance operations in advance to meet the most appropriate conditions.
The service concept investigated within this activity is going to be tested in the Andasol-3 power plant, currently under construction.
-âIf the results are in line with our expectations, we will use the resulting forecasting service to improve the operations of other CSP projects we are developing around the world,â says Benedikt Pulvermüller. âWe could even start providing these forecasting services to other CSP or Photovoltaic operatorsâ.
The CSP-FoSyS activity has just started its second phase, and it is run by Solar Millennium, a company new to the space arena specialised in the development and construction of innovative technologies for solar thermal power plants. They are supported by DLR-DFD and ESA.





 INTOGENER (INTegration of EO data and GNSS-R signals for ENERgy applications) focuses in the case of Chile. ENDESA, a Spanish utility owned mostly by the Italian Enel Group is de facto the largest utility in South America, being Chile one of the markets they operate. In Chile, more than 40 % of the national electricity mix comes from hydroelectricity power plants, being most of them located in the central area of the country. For the management of the power plants, all the utilities use currently a statistical model of the region. It is based on a limited set of in-situ measurements as well as previous yearsâ meteorological and hydrological information. The accuracy of the outcomes of this model differs up to 60 % with respect to reality. ENDESA is willing to find an alternative that can help them to manage their power plants in a more efficient way. Over the past decade, the electricity demand in Chile has grown at an average rate of 7 % per year, making mandatory an optimisation of the hydroelectrical resources in the short term to avoid further investment in fossil sources to fill the demand.
INTOGENER (INTegration of EO data and GNSS-R signals for ENERgy applications) focuses in the case of Chile. ENDESA, a Spanish utility owned mostly by the Italian Enel Group is de facto the largest utility in South America, being Chile one of the markets they operate. In Chile, more than 40 % of the national electricity mix comes from hydroelectricity power plants, being most of them located in the central area of the country. For the management of the power plants, all the utilities use currently a statistical model of the region. It is based on a limited set of in-situ measurements as well as previous yearsâ meteorological and hydrological information. The accuracy of the outcomes of this model differs up to 60 % with respect to reality. ENDESA is willing to find an alternative that can help them to manage their power plants in a more efficient way. Over the past decade, the electricity demand in Chile has grown at an average rate of 7 % per year, making mandatory an optimisation of the hydroelectrical resources in the short term to avoid further investment in fossil sources to fill the demand.


 Natural selection has taught birds to wait until the very last moment to turn in order to avoid predators. This has to be done in this way, because if they move before, predators will be still able to turn and catch them. Nowadays, as planes are becoming faster and more silent, birds, perceiving planes as possible predators, do not really have enough time to turn, and therefore, got struck by aircraf
Natural selection has taught birds to wait until the very last moment to turn in order to avoid predators. This has to be done in this way, because if they move before, predators will be still able to turn and catch them. Nowadays, as planes are becoming faster and more silent, birds, perceiving planes as possible predators, do not really have enough time to turn, and therefore, got struck by aircraf
 When talking about Civil Aviation we have to take into consideration liability issues, reports a specialised lawyer. For example, an airport operator's liability is usually dependant on the claimant proving the airport was at fault. In case of accident, passengers are going to make claims against airlines, and these are going to make claims against airport operators.
When talking about Civil Aviation we have to take into consideration liability issues, reports a specialised lawyer. For example, an airport operator's liability is usually dependant on the claimant proving the airport was at fault. In case of accident, passengers are going to make claims against airlines, and these are going to make claims against airport operators. IAP is pleased to announce the starting up of the
IAP is pleased to announce the starting up of the  Etihad Airways will install new state-of-the-art technology on its long and ultra long haul aircraft which can monitor the condition of passengers who display signs of sickness that might require immediate medical attention.
Etihad Airways will install new state-of-the-art technology on its long and ultra long haul aircraft which can monitor the condition of passengers who display signs of sickness that might require immediate medical attention.
